Bernoulli distribution is commonly used in statistics. It is a discrete probability distribution that conducts the outcome (single or failure) of a specific experiment. Its outcomes are usually labeled as “1” and “0”, where 1 symbolizes “success” and 0 defines “failure”. PyTorch provides the “torch.bernoulli()” method which enables users to generate binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution/
This article will exemplify the method to generate binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch.
How to Generate Binary Random Numbers from a Bernoulli Distribution in PyTorch?
To generate binary random numbers from a Bernoulli Distribution, follow the below-listed steps:
- Import PyTorch library
- Create/define the desired input tensor
- Generate binary random numbers using the “torch.bernoulli()” method
- Print the generated binary random numbers
Check out the examples below for a better understanding:
Example 1: Generate Binary Random Numbers From Bernoulli Distribution Using 1D Tensor
In the first section, we will define a 1D tensor and generate binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution using it.
Step 1: Import PyTorch Library
First, type the following line to import the “torch” library for generating binary numbers from the Bernoulli distribution:
import torch
Step 2: Define 1D Tensor
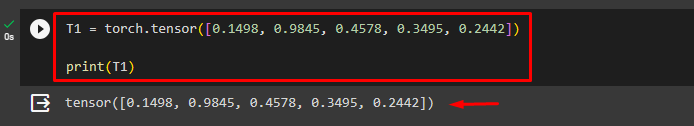
Then, define a desired 1D tensor and display its elements. Here, we are defining the following “T1” tensor from a list using the “torch.tensor()” function:
T1 = torch.tensor([0.1498, 0.9845, 0.4578, 0.3495, 0.2442])
print(T1)This has created a 1D tensor as seen below:
Step 3: Generate Binary Random Numbers
Now, utilize the “torch.bernoulli()” method and specify the input tensor to generate binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution:
random_num = torch.bernoulli(T1)
Step 4: Print Generated Random Numbers
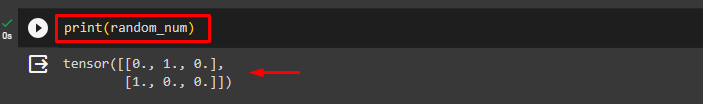
Finally, display the generated binary random numbers:
print(random_num)The below output displays the generated binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution:

Example 2: Generate Binary Random Numbers From Bernoulli Distribution Using 2D Tensor
In the second section, we will define a 2D tensor and generate binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution using it.
Step 1: Import PyTorch Library
First, install the “torch” library using the provided line:
import torch
Step 2: Define 2D Tensor
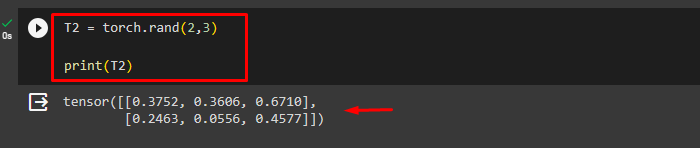
Next, define the desired 2D tensor and print its elements. Here, we are making a 2D tensor from random numbers via the “torch.rand()” function:
T2 = torch.rand(2,3)
print(T2)This has created a 2D tensor:
Step 3: Generate Binary Random Numbers
Now, generate binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution using the “torch.bernoulli()” method and specify the input tensor:
random_num = torch.bernoulli(T2)
Step 4: Print Generated Random Numbers
Finally, display the generated binary random numbers:
print(random_num)In the below output, the generated binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution can be seen:
We have efficiently explained the method of generating binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch.
Note: Click on the provided link to access our Google Colab Notebook.
Conclusion
To generate binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch, install the “torch” library. Then, define the desired tensor and view its elements. Next, use the “torch.bernoulli()” method and specify the input tensor to generate/create binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution. Lastly, print the generated binary random numbers. This article has exemplified the method to generate binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Bernoulli distribution in statistics?
A Bernoulli distribution is a discrete probability distribution that represents the outcome of an experiment with two possible outcomes, typically labeled as '1' for success and '0' for failure.
How does PyTorch enable the generation of binary random numbers?
PyTorch provides the 'torch.bernoulli()' method that allows users to generate binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch.
What is the significance of '1' and '0' in the Bernoulli distribution?
In the Bernoulli distribution, '1' typically represents 'success' and '0' represents 'failure' for the outcomes of the experiment.
How can I import the PyTorch library to generate binary random numbers?
To import the PyTorch library for generating binary random numbers, use the command 'import torch' in your Python code.
What are the steps to generate binary random numbers from a Bernoulli Distribution in PyTorch?
The steps include importing PyTorch library, defining the input tensor, using 'torch.bernoulli()' method to generate binary random numbers, and printing the generated numbers.
Can you provide an example of generating binary random numbers using a 1D tensor in PyTorch?
Yes, you can define a 1D tensor, apply the 'torch.bernoulli()' method on it, and print the generated binary random numbers as demonstrated in the example provided in the article.
What is the output format of the generated binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch?
The output format of the generated binary random numbers will be in the form of a PyTorch tensor with elements representing the binary values.
How can I check examples of generating binary random numbers from the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch?
You can refer to the examples provided in the article for a clear demonstration of how to generate binary random numbers using the Bernoulli distribution in PyTorch.